* TELEASSISTANCE
* TELE – EXPERTISE
* TELE – EDUCATION

DENTAL SURGERY AND DIAGNOSTIC RÖNTGEN CENTRE ∙ DR MARJANOVIĆ ∙
founded in 1999.
The recommended technique with a significantly reduced radiation field. The arrows indicate the reduction of the radiation field from the standard size of 15×30 cm and not by reducing the image. The upper parts of the facial bones and the cervical part of the spinal cord are not exposed to unnecessary radiation. Such an image can be digitally enlarged so that the blank area is not visible. By applying the digital method of the aforementioned technique, the exposure of children to X-rays is reduced by approximately 50-70%.
Scanographic imaging is essentially tomographic, only the orthopan tube is stationary at the moment of exposure
It is necessary to target the area in question
• The alveolar extension of the upper and lower jaws
• The maxillary sinus
• The TM joint
Since a very tight and strictly collimated beam of X-rays is focused, we get a sharper, less deformed image with higher contrast in the zone of dentition than with a large OPG. At the same time this technique of alveolar extensions replaces a large number of retroalveolar images.
• Zone 1 – encompasses the right ramus and the upper and lower right molars
• Zone 2 – upper-right molars and paramolars
• Zone 3 – upper and lower front
• Zone 4 – left upper and lower premolars and molars
• Zone 5 – the left ramus and molars
Tele – RTG analyses with selected points, curves and angles, standardized or done according to the therapist’s selection.
For a computer analysis of a digital image – an orthodontic craniometric analysis, it is sufficient to mark the craniometric points in order to obtain the desired analysis with a printout of the image, graphic and numeric values.
The processing of bone density in a localized osteosclerotic change. It aids the diagnosis of osteoporosis, osteosclerosis, as well as is determining the growth type of long bones. The graph was determined in the marked zone, juxtaposed with a radiologically healthy zone for the purpose of comparison.
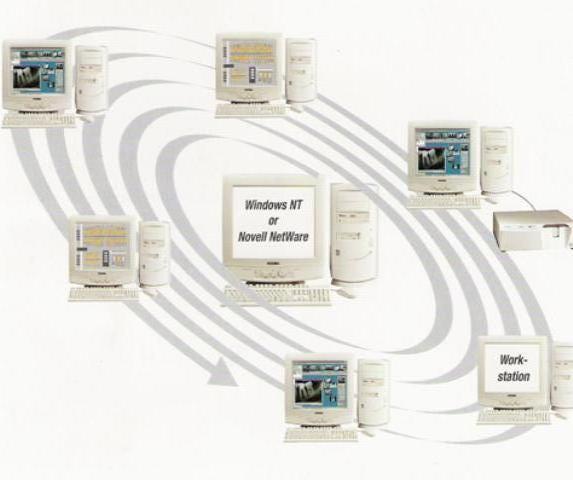
With the development of information technology and telecommunication it has become possible to create an internal network between therapists of different specialties, whereby it would be much faster to exchange results, referrals, X-rays, details on the course of the treatment and all other information for the purpose of additional consultations on possible therapies. This allows a continuity in further specialization which takes place on a daily basis in the course of dental practice.